In this era of social unrest and urbanisation, the effort to address global concerns about social tensions, environmental issues and saving natural resources has reached a large platform. It was during this phase that the concept of ‘sustainable development’ was globally introduced as a social goal. Rising temperatures and accelerated urbanisation are the major causes of failure to make a city sustainable. Today, every city in the world is implementing the smart city module to have all the infrastructural facilities, which also revolve around layers of sustainability. This offers an opportunity to investigate how social parameters help to create a sustainable environment affecting the wider aspects of urban cities.
In the Indian context, the development of large scale infrastructural facilities and urbanisation has overpowered the aspects of social and ecological balance to create a sustainable environment. In the current scenario, metro cities look like a patchwork created by bringing traditional, informal and new urban areas together. This phenomenon has led to an increase in the lack of socio-cultural and environmental aspects that create a sustainable environment. When sustainability is looked at through a social lens, it reflects a sense of motivation that enhances continuity and growth in its users, which is helpful for sustainable built outcomes. This can be observed in the evolution of public spaces from traditional use to their use in the modern day. This essay discusses the factors of traditional Indian cities that make them socially as well as environmentally sustainable, even when designers are struggling to make cities self-sustainable keeping in mind socio-cultural, economic, political and environmental aspects.
Evolution of Traditional Indian Cities
Water holds the central place in the practices and beliefs of different people, because it cleanses and washes away impurities and pollutants. It is believed that most traditional Indian cities evolved on the edges of water – i.e. seafront, riverfront and lakefronts – keeping sustainability in mind.
Water is the most essential part of everyone’s life; throughout history it has been the most influential aspect of life. Along with that, water is believed to be one of the most auspicious elements on earth having huge religious importance in India. During earlier times, civilisations flourished on the water’s edge because water was the predominant factor in the survival of humankind. The human response to water and different water bodies resulted in domestic needs. The ecological responses played significant roles:
1. Providing food from near the waterbodies
2. Vegetation growth on its banks
3. The cool surroundings and shaded environment

The relationship between these needs and waterbodies helped in the emergence of such spaces and architecture that was imperative in making it self-sustainable. Waterfronts are perceived very differently in the Indian setting and have a diverse context. During ancient times, waterfronts in the Indian context were never celebrated as a recreational public place. A waterfront is not very well emphasised in Indian culture compared to the western concept. Water and religion are intricately woven into the lifestyle of Indians. Along with that, due to the sub-tropical climate, the preference for waterfronts is more on the socio-cultural aspects such as bathing rituals. In the Indian context, it is believed that rivers are sacred and the step-wells have shrines and idols of Gods; lakes were used to offer prayers to water that was considered a God. Therefore, layers of activities along with built form typologies and their architectural responses co-exist.
In India, many cities have flourished on the banks of waterfronts. This essay talks about such a city that has evolved on the waterfront and the factors that have made the city socially and environmentally sustainable. Udaipur, also known as the Venice of the East, has evolved on the edge of Lake Pichola. The main feature of waterfronts is the physical accessibility to water that also leads to a specific response to the water’s edge. Therefore, particular architectural elements such as Ghats, Ovara (a gateway to access the water body), and bathing pavilions can be said to be the evolution of built form with architectural conceptions along the water’s edge.
Case Study: Udaipur, India
The city was founded as the capital of Mewar in 1559. The city of lakes, Udaipur is situated in a bowl-shaped basin, which sits on the eastern side of the hills of the Aravalli range in southern Rajasthan. Udaipur has the distinctive features of the lakes: it is geographically secluded due to the natural enclosure formed by the surrounding hills and the altitude, and its rugged terrain creates favourable site conditions for the medieval settlement in terms of natural defense, micro-climate and opportunities to develop itself.
So, the lakes play an important role to provide visual structure and orientation, cues that lend to visual and psychological relief in the hot and dry climate.
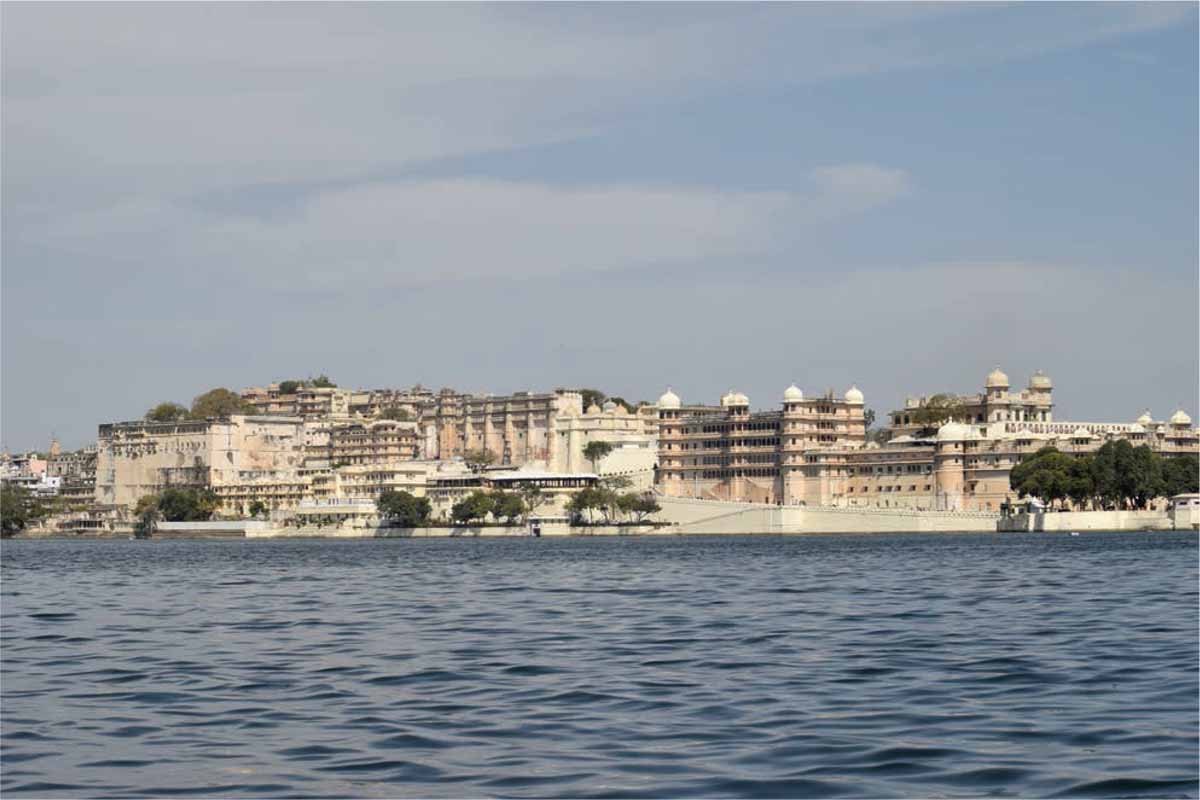

City Palace, Udaipur
Udaipur is called the ‘City of Lakes’ and ‘Venice of the East’ all over the world due to its specific topography and natural beauty with its eight lakes. The lakes are: Pichola, Swaroop Sagar, Rang Sagar, Fatehsagar, Badi, Udaisagar, Chota Madar and Bada Madar. All these lakes form a chain in the saucer-shaped valley. So, the inner Girwa Plain is surrounded by the western and central hills having its water drained into the Ahar River. The interconnected network of lakes emerged for recreation and irrigation. The three major lakes of the city are Pichola and Fatehsagar that are in the city, and Udaisagar which is on the periphery of the city. They are either interconnected or feed other smaller lakes. Earlier, there were numerous Wells and Bavdis (step wells), which were the only source of drinking water. Therefore, water from these lakes was not utilised for drinking purposes as is their current use. The lakes are the backbone of Udaipur because they provide the city with surface water resources, ecosystems and tourism for the local economy.

Timeline of the city
The Skyline of the City visible from the western side not only presents an aesthetic experience, but it also speaks of the political set up of that era. The main elements of the city consisted of gates, chowks, temples and ghats. The formation of the streets had a unique pattern due to the topography of the city and the significant position of the two most important built forms: the Palace and Jagdish Mandir. All the primary streets started from the Gates and terminated at Jagdish Chowk where the temple is located, thus forming a radial pattern. The secondary, semi-commercial streets lead from the market area to the residential areas. Thus, a house, the smallest component of a city structure, is related to the whole city in an organic manner by the hierarchical order of streets.
The edge of Lake Pichola defines the city of Udaipur due to the sitting of the Palace on the south-east side. Later on, the city started spreading out, where the edge on the northern side consists of many religious built forms. Therefore, the edge of Lake Pichola serves various usage purposes other than bathing and washing. The edge in Udaipur is not marked by a continuous promenade or natural banks in the form of ghats. There are a few public and private ghats lining the edge. In the current scenario also, the ghats and temples play a vital role in creating public spaces for the residents of the city as well as the tourists.
These spaces have been active participants to create a socially sustainable environment since ancient times. They not only emerge as an identity to the city, but also provide room for various activities for the people.
Gangaur Ghat, Udaipur
Gangaur Ghat is one such example that is located near the Jagdish Chowk area and it is also known for the Bagore Ki Haveli located next to the ghat. It was built by Maharana Shakti Singh in 1878 in a place where festivals like the Gangaur Festival and other rituals have been celebrated since the 16th century AD. After the festival of Holi, Gangaur is the most colourful festival of Rajasthan in which ‘Gan’ symbolises Lord Shiva and ‘Gaur’ symbolizes Parvati. Unmarried women of the royal palaces and from all over the city worship the goddess to be blessed with husbands of their choice, while married women pray for the well-being of their husbands. On the final day, rituals similar to marriage are carried out with a procession from the city centre to the lake edges, or the ghats.
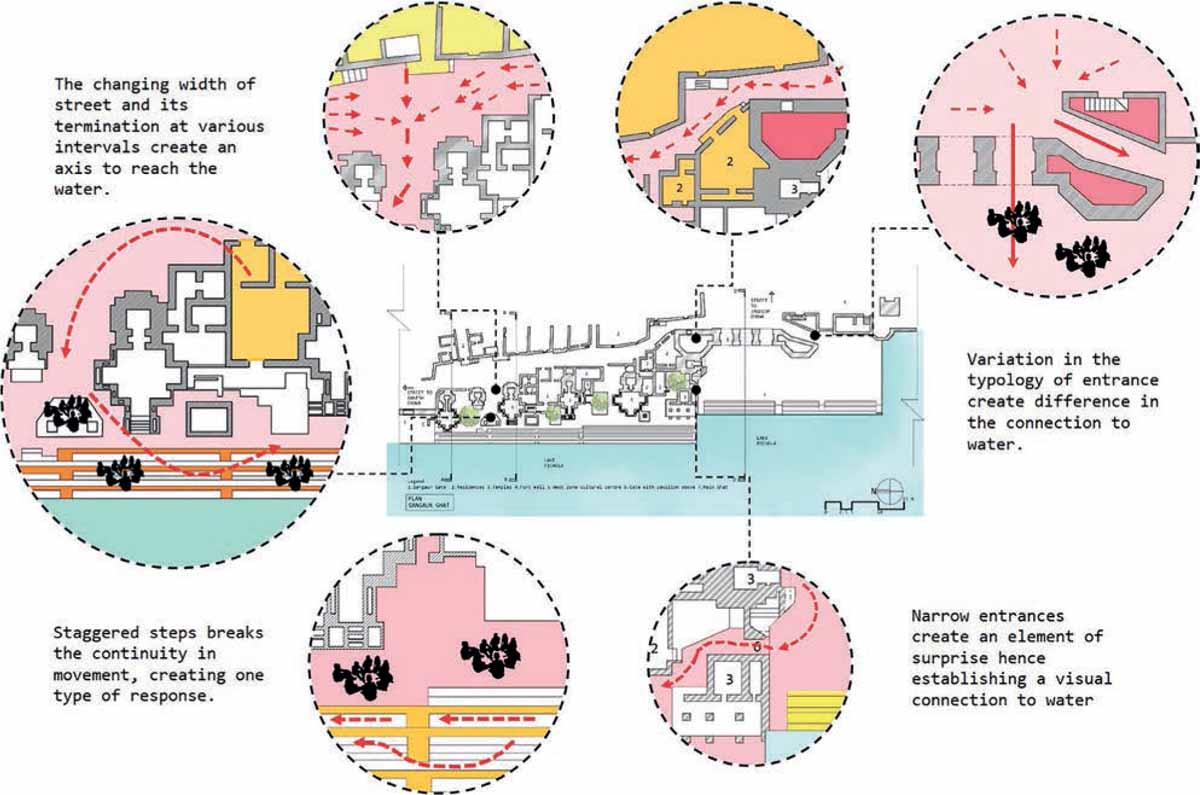
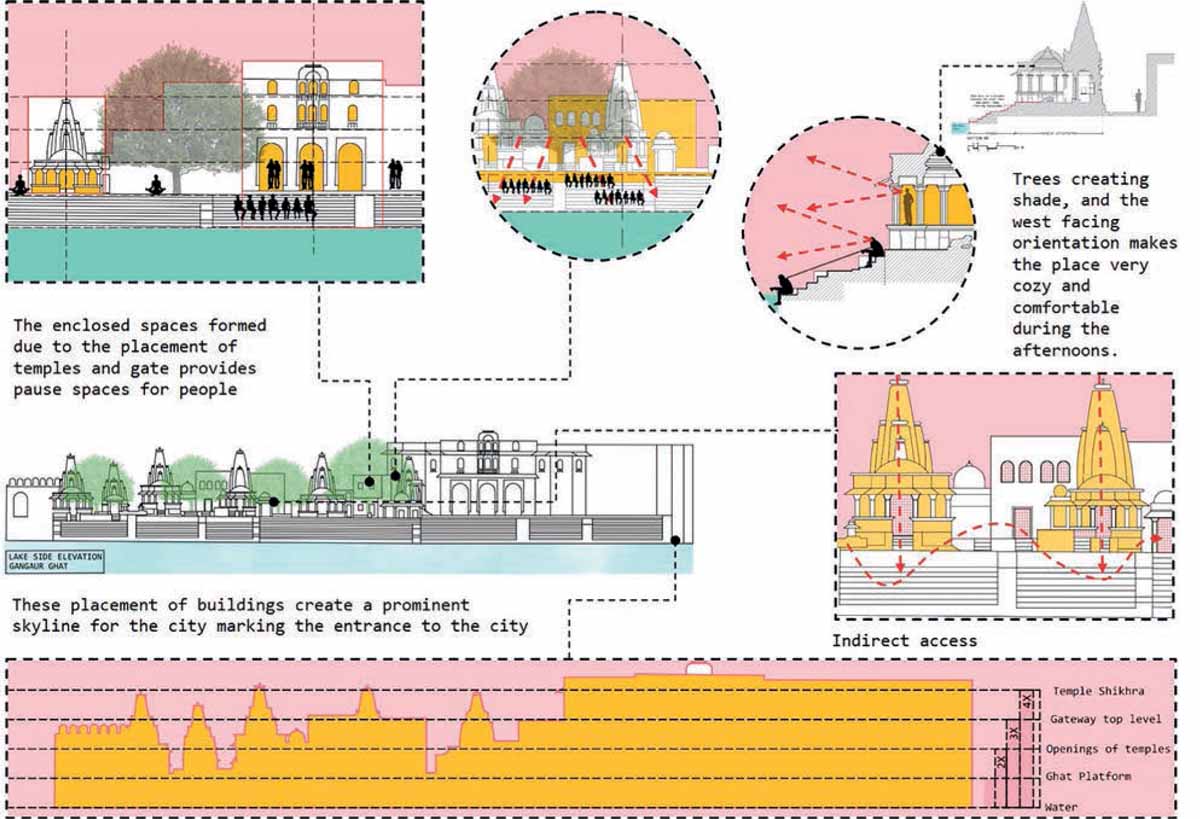
The street leading to the ghat is a secondary street that branches out from the Tripoliya Gate Street meeting at the junction of Jagdish Chowk. The ghats form a city level public open space, which also has deep religious importance to the city connected to the water. The ghat acts as a threshold between the water and the city, which becomes the interface in this case. Gangaur Ghat is oriented east-west, and the centres of all the temples look towards the lake, the orientation of all the temple structures and the main ghat’s built form is perpendicularly placed, inviting people to walk from the ghat to the lake. There are layers of built form prevailing at the ghat, which provides different views. On a larger scale, the panoramic view of the front side i.e. Hanuman Ghat to Ambrai Ghat, is visible along with the magnificent Lake Pichola. There are a series of residences on the secondary street that are accompanied by the temples on its front forming the enclosed spaces. This combination of the built form and void spaces makes the form and massing at the Gangaur Ghat.
The elements such as columns and plinths make the temples act as a filter in a visual and sacred manner.
Further, these temples are attached to the steps, which give an elevated open platform to the place. Therefore, it can be perceived that there lies a hierarchy of built space and semi-open space, which ends with an open space that makes the interface with the water.
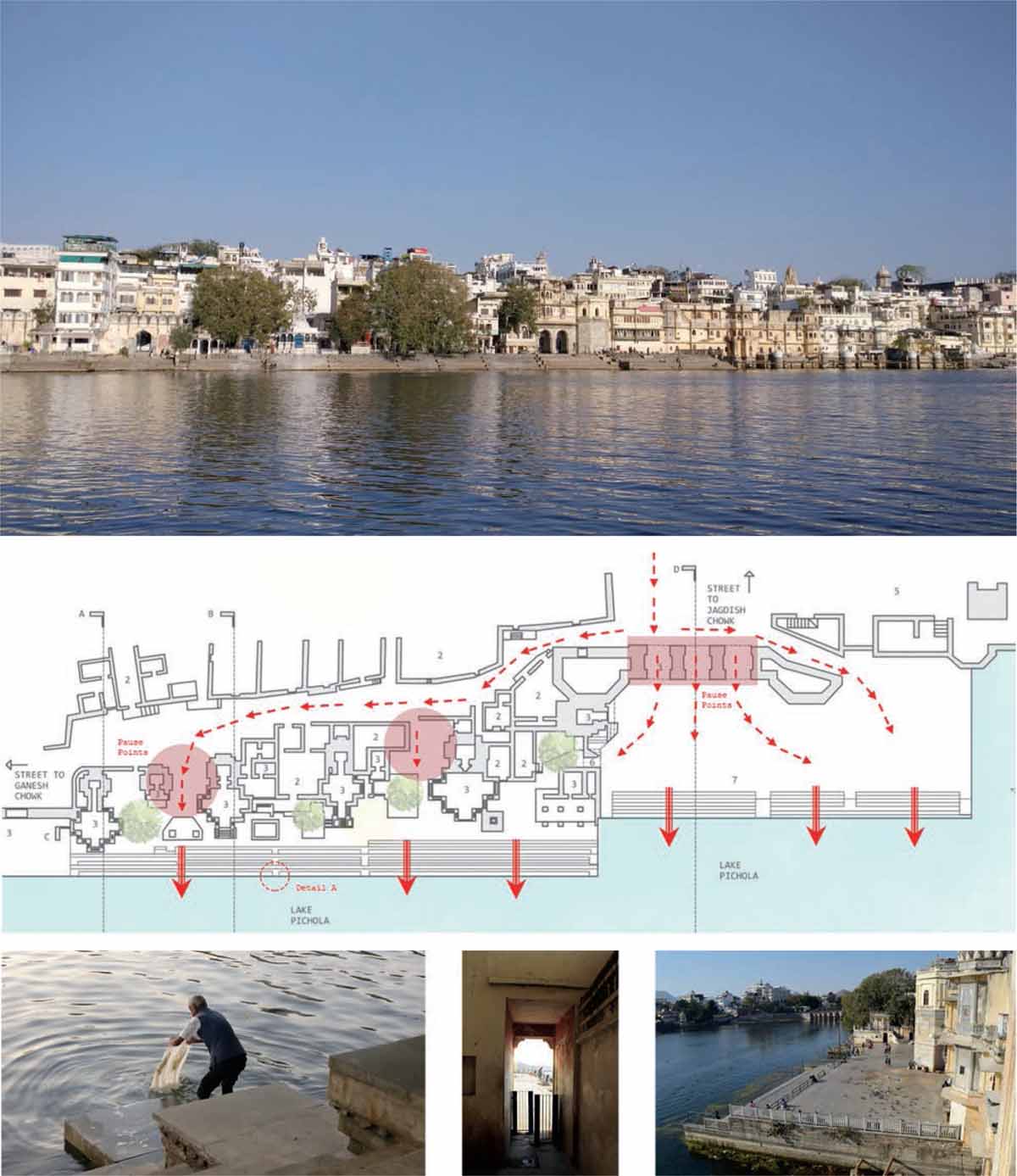
Bottom: Accessibility to Gangaur Ghat, Udaipur
Accessibility to Gangaur Ghat, Udaipur
The organisation of the ghat area can be divided into two parts: the elevated public platform and the religious temple structures. The placement of these structures forms enclosed spaces that help reach the water. There is a hierarchy of nature of spaces created due to the organization of the built forms in response to water. This nature of spaces changes from private to semi-open to open in the case of residences, temple structures and ghats. During the initial growth of the city, all the temples and shrines were built facing the edge of the lake, because of the sacredness of the water, and water was needed to be accessible for religious purposes. Then, the ghat was built due to the existing topography of the lake. Further, the residences were built behind the temples, which now form enclosed spaces.
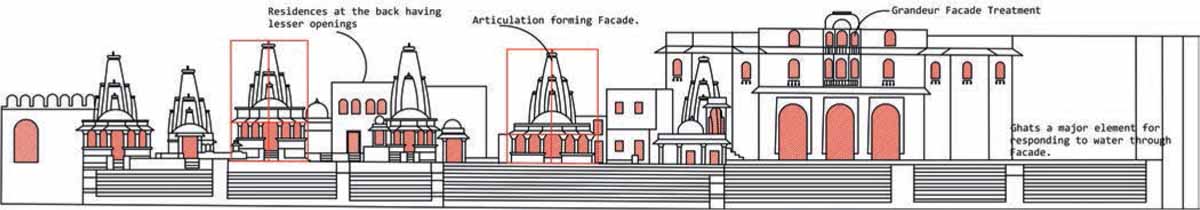
Façade at Gangaur Ghat, Udaipur
Gangaur Ghat is a city-level public place that is directly connected to Lake Pichola through gradual steps. During the day, numerous activities are afoot. In the morning, religious activities are performed in the temple, which involves people’s participation inside the built form and on the ghats. Daily rituals are performed on the ghats like feeding the birds, worshiping the water, bathing, washing clothes, etc. At noon, the entire place turns calm, and people’s participation is seen more towards the ghat area near the temples due to the shade provided. Again, in the evening, the ghat turns into a spiritual place due to the evening rituals at the temple. At night, in the late hours due to brighter lights on the main ghat, people are often seen spending their leisure time near the water.
Conclusion
Water and the waterfront is the common factor around which the parameters of social and environmental sustainability revolve. In the given case, there has been a constant evolution of the environmental aspects. The fundamentals of evolution for social aspects remain constant with the little differences that bring out a varied type of urban form and architecture, which further leads to using similar spaces differently. One can find the ecological balance that is created with the traditional architectural response to the climate having the perceptions of safety, ownership and governance.
Udaipur as a city has sustained itself for so long due to multiple factors such as climate resilience, easy access and connections, responding to the water’s edge, multifunctional use of spaces with activities, spaces that emerged due to socio-cultural importance, active community participation and interaction.
At the larger level, the urban morphology may look fragmented, but at the neighbourhood level, it has emerged as a strong, cohesive social and spatial unit. Along with that, the safety and security aspect is rarely compromised in such traditional cities. The recreational open spaces are rarely found to be dead during the day or the night. This also increases the social interaction of the people with the spaces, hence creating a socially sustainable place. The major density of people is found to be near the water’s edge, which generates the occupational opportunities for the residents and a wide range of choices for the visitor. The religious aspect cannot be overlooked in these cases where the temple architecture not only breaks the monotony of the skyline but also brings in divinity to create a peaceful environment. Hence, it can be said that social sustainability is as important as environmental sustainability to make cities sustainable.
References
-Moore, C. W. (1994). Water and Architecture. New York: Harry N. Abrams, Incorporated.
-Samant, S. (2010). Reflections on Water: Architectural Manifestations in the Historic and Cultural Quarter along Lake Pichola in Udaipur. Journal of Sustainable development, 1-8.
-Sen, R. (2000). Attributes of Place - The urban space in the traditional Indian city of Udaipur, Diploma Dissertation, Ahmedabad: CEPT, India.


Comments (0)